Zollinger Ellison Syndrome
We are familiar with the term peptic ulcer, a condition where mucosal erosion occurs due to excess acid in the stomach. The presence of any tumor can induce the excess production of gastric acid.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES) is a rare condition where we can see all these factors together, that is
- Severe peptic ulcer
- Hypersecretion of gastric acid
- Presence of gastrinoma (gastrin producing tumors)
And these three factors are known as the triad of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES).
Where can this tumor occur?
In about 75% of cases, the tumor occurs in the duodenum making it the most common site. The pancreas is the second most common region to have gastrinoma accounting for 25% of cases. The remaining 5% of cases can have tumors in other sites.
Etiology
The exact etiology is unknown. However, an association with MEN - 1 (Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia 1) is often seen. It is caused by inactivating mutations of the MEN1 tumor suppressor gene found on the long arm of chromosome 11q13.
Wisdom: This gene encodes for Menin, which has an important role in DNA replication and transcriptional regulation.
Hence, it is very important to always suspect MEN syndrome in all cases of ZES and do further investigations to rule out the same.
Females are slightly more affected than males, and the majority of patients are diagnosed between ages 30 and 50.
Pathophysiology
As we know, parietal cells secrete acid on stimulation by histamine and gastrin.
In ZES there are increased levels of gastrin which are produced by the tumors present in the pancreas and duodenum. Thus, in ZES there is hyperstimulation of parietal cells resulting in increased secretion of acid by them.
The increased gastric acid output leads to peptic ulcer, GERD, and other clinical manifestations of ZES.
Symptoms
Most of the complaints are due to increased levels of gastric acid.
Abdominal pain is the most common clinical presentation due to irritation caused by excess acid.
Patients can have diarrhea due to defective digestion.
Oesophageal symptoms are due to the regurgitation of acid from the stomach.
- Acid reflux and heartburn
- Burning, aching, discomfort in the upper abdomen
- Bleeding in the digestive tract
- Nausea and vomiting
Other symptoms indicating malignancy like decreased appetite, unexplained weight loss are also seen.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is done based on clinical history and investigations.
Blood test- shows elevated gastrin levels indicative of gastrin secreting tumors.
Secretin stimulation test- In this, an injection of hormone secretin is given and blood gastrin level is measured. If ZES is present, injection of secretin will increase the gastrin levels in the body
Upper GI endoscopy
This is done to detect the presence and extent of ulceration and tumor in GIT.
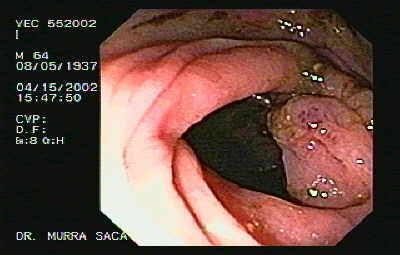
Endoscopic USG
It is used for closer inspection of the organ thereby making it easier to identify the site of the tumor.
You can also use this opportunity to collect biopsy samples efficiently. which can further undergo cytological studies and reveal whether the tumor is malignant or benign.
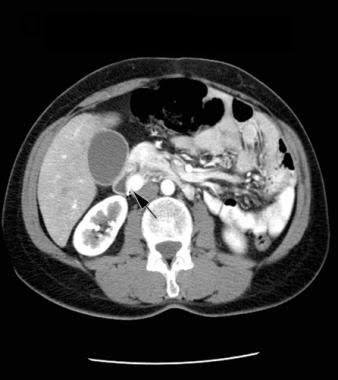
Radiological imaging test
X-Ray, CT, MRI can be done to locate the tumors and their extent.
Treatment
As there are no preventive strategies that are identified to cure Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, early detection should be done. Early detection and appropriate treatment will prevent metastasis of the tumor to other organs. Treatment of peptic ulcers is also important because chronic peptic ulcers can lead to complications like gastric carcinoma, perforation, etc.
So treatment aims to
- get symptomatic relief,
- cut down the growth rate of tumors, and
- prevent metastasis.
Medical treatment
It is directed towards reducing basal acid output to < 10 mmol/L thereby controlling symptoms and preventing complications.
This is achieved by treatment with Omeprazole and is usually given life long. It is more effective than H2 blockers in controlling hyperacidity in this case. Even though other proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers can also be used to treat the peptic ulcer.
If the tumor extent is less, chemotherapy can be tried to control the growth of the tumor.
Surgical treatment
In the case of bulky tumors, removal of tumors (debulking) is done to keep the disease in control. Destruction of tumors by embolization or radiofrequency ablation can also be done.
If the tumor invades the liver and affects its function, liver transplantation is to be done.
References
- Harrison principle of internal medicine 20th edition
- Robbins basic pathology 9th edition
- Essentials of medical pharmacology-K D Tripathi 7th edition
- Bailey & Love’s short practice of surgery 27th edition
Authors footnote
ZES is almost always associated with MEN-1 syndrome (Wermer’s syndrome). The organs involved in MEN -1 can be remembered with 3Ps
- Parathyroid adenoma
- Pituitary adenoma (Prolactinoma being most common)
- Pancreas gastrinoma
Also, the pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor is the most common cause of death in MEN - 1 syndrome.
Feel free to click on the references for a more in-depth reading if you so desire. If you feel any information can be added or that there are any inadvertent errors, feel free to let us know in the comments below or bring it to our notice via support@medicalwizardry.com
Even otherwise, feel free to use the comments section for discussion.
We would love to hear from you. Reach out to us via admin@medicalwizardry.com to share any random gibberish/ideas that you would like implemented.
